
When it comes to plastics, there are many variations, each with its unique properties and applications. One such versatile polymer is polypropylene, often referred to as PP.
In this blog, we will dive deep into the world of polypropylene, exploring its types, uses, and key characteristics.
Understanding Polypropylene (PP):
Polypropylene is a type of thermoplastic polymer characterized by its chemical structure, which consists of repeating units of propylene monomers (C3H6)n. This molecular arrangement imparts remarkable properties to PP, making it a popular choice across various industries.
Types of Polypropylenes:
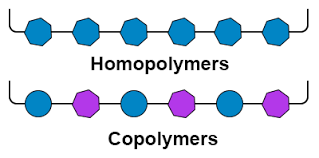
Polypropylene comes in different types, each tailored to specific applications. The article outlines several common variations:
Homopolymer PP: This type of PP consists of only propylene monomers and is known for its high stiffness, strength, and temperature resistance. Homopolymer PP is commonly used in automotive parts, packaging, and consumer goods.
Random Copolymer PP: Random copolymer PP includes a small percentage of ethylene monomers in addition to propylene. This modification improves its clarity, impact resistance, and flexibility, making it suitable for applications like clear packaging, housewares, and film.
Block Copolymer PP: Block copolymer PP features long sequences of propylene and ethylene monomers, resulting in excellent impact resistance and transparency. This type finds application in food containers and medical devices.
Key Characteristics of PP:
High Chemical Resistance: PP is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it ideal for use in chemical storage tanks and pipes.
Low Density: It has a low density, which translates to lightweight yet durable products.
Good Thermal Resistance: PP can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications involving hot liquids or environments.
Recyclability: PP is recyclable, contributing to sustainability efforts in various industries.
Low Moisture Absorption: It exhibits minimal moisture absorption, maintaining its structural integrity even in humid conditions.
Applications of Polypropylene:
The versatility of PP opens the door to a multitude of applications,
Packaging: PP is widely used in the packaging industry for bottles, caps, containers, and films due to its excellent barrier properties and clarity.
Automotive: It finds its place in automotive interiors and under-the-hood components for its heat resistance and strength.
Textiles: PP is used to create fabrics, ropes, and carpets due to its resistance to moisture and abrasion.
Medical Devices: Its high purity and chemical resistance make it suitable for medical applications like syringes and test tubes.
Construction: PP pipes and fittings are common in plumbing and construction due to their durability and corrosion resistance.
Consumer Goods: PP is a staple in the production of everyday items like toys, kitchenware, and luggage.
In summary, polypropylene (PP) stands as a testament to the remarkable diversity of plastic materials. Its various types and exceptional characteristics have solidified its place in industries ranging from packaging and automotive to textiles and construction.

As we continue to explore and innovate, PP will undoubtedly play an integral role in shaping our future.
The next time you encounter a transparent food container, a durable automotive component, or a comfortable carpet, you might just be appreciating the versatility of polypropylene, quietly at work in the background.